|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
|
|
+.. _doc_visual_shader_plugins:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Visual Shader Plugins
|
|
|
+=====================
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Introduction
|
|
|
+------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Visual Shader Plugins are used to create custom Visual Shader nodes in GDScript.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The creation process is different from EditorPlugins - you simply create and save a script file and it will be ready to use.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Visual Shader Plugin
|
|
|
+--------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+This short tutorial will explain how to make a Perlin-3D noise node (original code from https://github.com/curly-brace/Godot-3.0-Noise-Shaders/blob/master/assets/gpu_noise_shaders/classic_perlin3d.tres).
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Create a sprite and assign a :ref:`ShaderMaterial <class_ShaderMaterial>` to its material slot:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/visual_shader_plugins_start.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Assign :ref:`VisualShader <class_VisualShader>` to the shader slot of the material:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/visual_shader_plugins_start2.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Don't forget to change its mode to CanvasItem (if you are using a sprite):
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/visual_shader_plugins_start3.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Create a script which derives from :ref:`VisualShaderNodeCustom <class_VisualShaderNodeCustom>`. This is all you need to initialize your plugin.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+::
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ # PerlinNoise3D.gd
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ tool
|
|
|
+ extends VisualShaderNodeCustom
|
|
|
+ class_name VisualShaderNodePerlinNoise3D
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_name():
|
|
|
+ return "PerlinNoise3D"
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_category():
|
|
|
+ return "MyShaderNodes"
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_description():
|
|
|
+ return "Classic Perlin-Noise-3D function (by Curly-Brace)"
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_return_icon_type():
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_SCALAR
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_input_port_count():
|
|
|
+ return 4
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_input_port_name(port):
|
|
|
+ match port:
|
|
|
+ 0:
|
|
|
+ return "uv"
|
|
|
+ 1:
|
|
|
+ return "offset"
|
|
|
+ 2:
|
|
|
+ return "scale"
|
|
|
+ 3:
|
|
|
+ return "time"
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_input_port_type(port):
|
|
|
+ match port:
|
|
|
+ 0:
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_VECTOR
|
|
|
+ 1:
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_VECTOR
|
|
|
+ 2:
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_SCALAR
|
|
|
+ 3:
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_SCALAR
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_output_port_count():
|
|
|
+ return 1
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_output_port_name(port):
|
|
|
+ return "result"
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_output_port_type(port):
|
|
|
+ return VisualShaderNode.PORT_TYPE_SCALAR
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_global_code(mode):
|
|
|
+ return """
|
|
|
+ vec3 mod289_3(vec3 x) {
|
|
|
+ return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 mod289_4(vec4 x) {
|
|
|
+ return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 permute(vec4 x) {
|
|
|
+ return mod289_4(((x*34.0)+1.0)*x);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 taylorInvSqrt(vec4 r) {
|
|
|
+ return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec3 fade(vec3 t) {
|
|
|
+ return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ // Classic Perlin noise
|
|
|
+ float cnoise(vec3 P) {
|
|
|
+ vec3 Pi0 = floor(P); // Integer part for indexing
|
|
|
+ vec3 Pi1 = Pi0 + vec3(1.0); // Integer part + 1
|
|
|
+ Pi0 = mod289_3(Pi0);
|
|
|
+ Pi1 = mod289_3(Pi1);
|
|
|
+ vec3 Pf0 = fract(P); // Fractional part for interpolation
|
|
|
+ vec3 Pf1 = Pf0 - vec3(1.0); // Fractional part - 1.0
|
|
|
+ vec4 ix = vec4(Pi0.x, Pi1.x, Pi0.x, Pi1.x);
|
|
|
+ vec4 iy = vec4(Pi0.yy, Pi1.yy);
|
|
|
+ vec4 iz0 = vec4(Pi0.z);
|
|
|
+ vec4 iz1 = vec4(Pi1.z);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 ixy = permute(permute(ix) + iy);
|
|
|
+ vec4 ixy0 = permute(ixy + iz0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 ixy1 = permute(ixy + iz1);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 gx0 = ixy0 * (1.0 / 7.0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 gy0 = fract(floor(gx0) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
|
|
|
+ gx0 = fract(gx0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 gz0 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx0) - abs(gy0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 sz0 = step(gz0, vec4(0.0));
|
|
|
+ gx0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gx0) - 0.5);
|
|
|
+ gy0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gy0) - 0.5);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 gx1 = ixy1 * (1.0 / 7.0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 gy1 = fract(floor(gx1) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
|
|
|
+ gx1 = fract(gx1);
|
|
|
+ vec4 gz1 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx1) - abs(gy1);
|
|
|
+ vec4 sz1 = step(gz1, vec4(0.0));
|
|
|
+ gx1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gx1) - 0.5);
|
|
|
+ gy1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gy1) - 0.5);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec3 g000 = vec3(gx0.x,gy0.x,gz0.x);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g100 = vec3(gx0.y,gy0.y,gz0.y);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g010 = vec3(gx0.z,gy0.z,gz0.z);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g110 = vec3(gx0.w,gy0.w,gz0.w);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g001 = vec3(gx1.x,gy1.x,gz1.x);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g101 = vec3(gx1.y,gy1.y,gz1.y);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g011 = vec3(gx1.z,gy1.z,gz1.z);
|
|
|
+ vec3 g111 = vec3(gx1.w,gy1.w,gz1.w);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec4 norm0 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g000, g000), dot(g010, g010), dot(g100, g100), dot(g110, g110)));
|
|
|
+ g000 *= norm0.x;
|
|
|
+ g010 *= norm0.y;
|
|
|
+ g100 *= norm0.z;
|
|
|
+ g110 *= norm0.w;
|
|
|
+ vec4 norm1 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g001, g001), dot(g011, g011), dot(g101, g101), dot(g111, g111)));
|
|
|
+ g001 *= norm1.x;
|
|
|
+ g011 *= norm1.y;
|
|
|
+ g101 *= norm1.z;
|
|
|
+ g111 *= norm1.w;
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ float n000 = dot(g000, Pf0);
|
|
|
+ float n100 = dot(g100, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.yz));
|
|
|
+ float n010 = dot(g010, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.y, Pf0.z));
|
|
|
+ float n110 = dot(g110, vec3(Pf1.xy, Pf0.z));
|
|
|
+ float n001 = dot(g001, vec3(Pf0.xy, Pf1.z));
|
|
|
+ float n101 = dot(g101, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.y, Pf1.z));
|
|
|
+ float n011 = dot(g011, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.yz));
|
|
|
+ float n111 = dot(g111, Pf1);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ vec3 fade_xyz = fade(Pf0);
|
|
|
+ vec4 n_z = mix(vec4(n000, n100, n010, n110), vec4(n001, n101, n011, n111), fade_xyz.z);
|
|
|
+ vec2 n_yz = mix(n_z.xy, n_z.zw, fade_xyz.y);
|
|
|
+ float n_xyz = mix(n_yz.x, n_yz.y, fade_xyz.x);
|
|
|
+ return 2.2 * n_xyz;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ """
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _get_code(input_vars, output_vars, mode, type):
|
|
|
+ return output_vars[0] + " = cnoise ( vec3 ( ( %s.xy + %s.xy ) * %s, %s ) ) * 0.5 + 0.5" % [input_vars[0], input_vars[1], input_vars[2], input_vars[3]]
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Save it and open the visual shader. You should see your new node type inside the member's dialog (if you can't see your new node, try restarting the editor):
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/visual_shader_plugins_result1.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
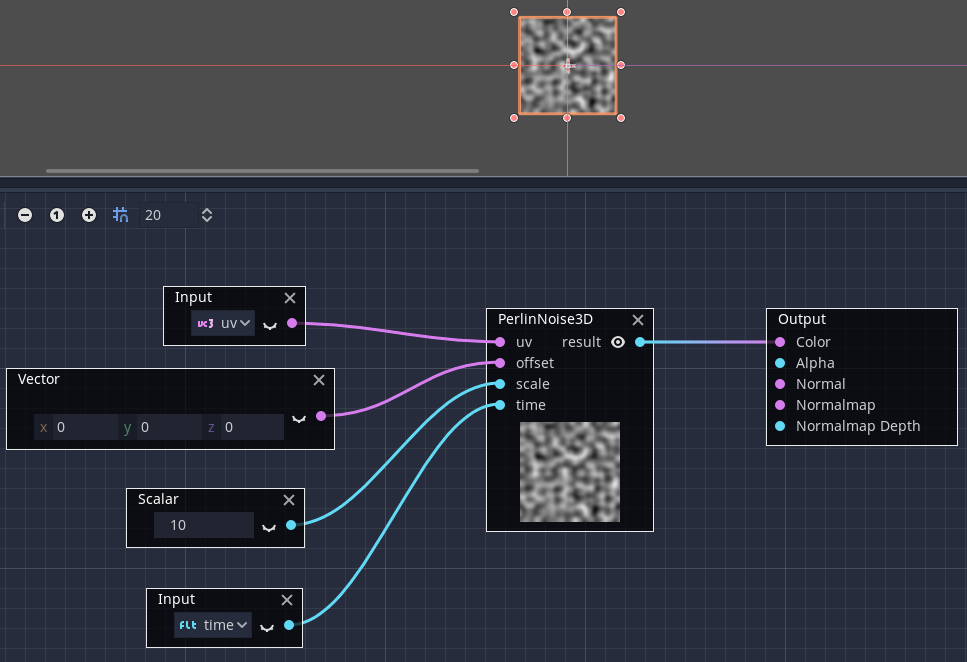
+Place it on a graph and connect the required ports:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/visual_shader_plugins_result2.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+That is everything you need to do, as you can see it is very easy to create your own custom VisualShader nodes!
|