|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
|
|
|
+.. _doc_navigation_overview_2d:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Introduction
|
|
|
+===================
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Godot provides multiple objects, classes and servers to facilitate grid-based or mesh-based navigation
|
|
|
+and pathfinding for 2D and 3D games. The following section provides a quick overview over all available
|
|
|
+navigation related objects in Godot for 2D scenes and their primary use.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+2D Navigation Overview
|
|
|
+----------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Godot provides the following objects and classes for 2D navigation:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`Astar2D<class_Astar2D>`
|
|
|
+ ``Astar2D`` objects provide an option to find the shortest path in a graph of weighted **points**.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ The AStar2D class is best suited for cellbased 2D gameplay that does not require actors to reach any possible position within an area but only predefined, distinct positions.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`NavigationServer2D<class_NavigationServer2D>`
|
|
|
+ ``NavigationServer2D`` provides a powerful server API to find the shortest path between two positions on a area defined by a navigation mesh.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ The NavigationServer is best suited for 2D realtime gameplay that does require actors to reach any possible position within an navmesh defined area.
|
|
|
+ Meshbased navigation scales well with large gameworlds as a large area can often be defined with a single polygon when it would require many, many grid cells.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ The NavigationServer holds different navigation maps that each consist of regions that hold navigation mesh data.
|
|
|
+ Agents can be placed on a map for avoidance calculation.
|
|
|
+ RIDs are used to reference the internal maps, regions and agents when communicating with the server.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ The following NavigationServer RID types are available.
|
|
|
+ - NavMap RID
|
|
|
+ Reference to a specific navigation map that holds regions and agents.
|
|
|
+ The map will attempt to join changed navigation meshes of regions by proximity.
|
|
|
+ The map will synchronise regions and agents each physics frame.
|
|
|
+ - NavRegion RID
|
|
|
+ Reference to a specific navigation region that can hold navigation mesh data.
|
|
|
+ The region can be enabled / disabled or the use restricted with a navigationlayer bitmask.
|
|
|
+ - NavAgent RID
|
|
|
+ Reference to a specific avoidance agent with a radius value use solely in avoidance.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The following SceneTree Nodes are available as helpers to work with the NavigationServer2D API.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`NavigationRegion2D<class_NavigationRegion2D>` Node
|
|
|
+ A Node that holds a NavigationPolygon resource that defines a navigation mesh for the NavigationServer2D.
|
|
|
+ The region can be enabled / disabled.
|
|
|
+ The use in pathfinding can be further restricted through the navigationlayers bitmask.
|
|
|
+ Regions can join their navigation meshes by proximity for a combined navigation mesh.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`NavigationAgent2D<class_NavigationAgent2D>` Node
|
|
|
+ An optional helper Node to facilitate common NavigationServer2D API calls for pathfinding and avoidance
|
|
|
+ for a Node2D inheriting parent Node.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`NavigationObstacle2D<class_NavigationObstacle2D>` Node
|
|
|
+ A Node that acts as an agent with avoidance radius, to work it needs to be added under a Node2D
|
|
|
+ inheriting parent Node. Obstacles are intended as a last resort option for constantly moving objects
|
|
|
+ that cannot be re(baked) to a navigation mesh efficiently. This node also only works if RVO processing
|
|
|
+ is being used.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The 2D navigationm eshes are defined with the following resources:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- :ref:`NavigationPolygon<class_NavigationPolygon>` Resource
|
|
|
+ A resource that holds 2D navigation mesh data and provides polygon drawtools to define navigation areas inside the Editor as well as at runtime.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ - The NavigationRegion2D Node uses this resource to define its navigation area.
|
|
|
+ - The NavigationServer2D uses this resource to update navmesh of individual regions.
|
|
|
+ - The TileSet Editor creates and uses this resource internally when defining tile navigation areas.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Setup for 2D scene
|
|
|
+------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The following steps show the basic setup for a minimum viable navigation in 2D that uses the
|
|
|
+NavigationServer2D and a NavigationAgent2D for path movement.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1.) Add a NavigationRegion2D Node to the scene.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+2.) Click on the region node and add a new NavigationPolygon Resource to the region node
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/nav_2d_min_setup_step1.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
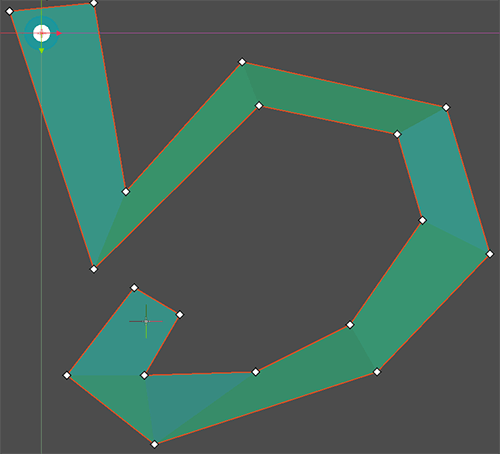
+3.) Define the moveable navigation area with the NavigationPolygon draw tool
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/nav_2d_min_setup_step2.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. note::
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ The navigation mesh defines the area where an actor can stand and move with its center.
|
|
|
+ Leave enough margin between the navpolygon edges and collision objects to not get path following actors repeatedly stuck on collision.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
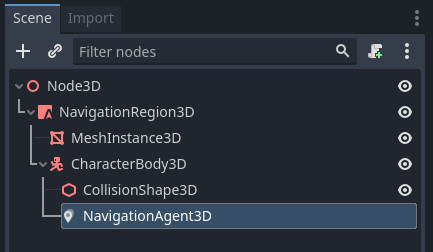
+4.) Add a CharacterBody2D below the region node with a basic collision shape and a sprite or mesh for visuals.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+5.) Add a NavigationAgent2D node below the character node
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. image:: img/nav_2d_min_setup_step3.png
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+6.) Add the following script to the CharacterBody2D node. Set a movement target with the set_movement_target() function after the scene has fully loaded and the NavigationServer had time to sync.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. note::
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ On the first frame the NavigationServer map has not synchronised region data and any path query will return empty.
|
|
|
+ Use ``await get_tree().physics_frame`` to pause scripts until the NavigationServer had time to sync.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+.. tabs::
|
|
|
+ .. code-tab:: gdscript GDScript
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ extends CharacterBody2D
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ var movement_speed : float = 200.0
|
|
|
+ var movement_target_position : Vector2 = Vector2(60.0,180.0)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ @onready var navigation_agent : NavigationAgent2D = $NavigationAgent2D
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _ready():
|
|
|
+ # these values need to be adjusted for the actor's speed
|
|
|
+ # and the navpolygon layout as each crossed edge will create a path point
|
|
|
+ # If the actor moves to fast it might overshoot
|
|
|
+ # multiple path points in one frame and start to backtrack
|
|
|
+ navigation_agent.path_desired_distance = 4.0
|
|
|
+ navigation_agent.target_desired_distance = 4.0
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ # make a deferred function call to assure the entire Scenetree is loaded
|
|
|
+ call_deferred("actor_setup")
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func actor_setup():
|
|
|
+ # wait for the first physics frame so the NavigationServer can sync
|
|
|
+ await get_tree().physics_frame
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ # now that the navigation map is no longer empty set the movement target
|
|
|
+ set_movement_target(movement_target_position)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func set_movement_target(movement_target : Vector2):
|
|
|
+ navigation_agent.set_target_location(movement_target)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ func _physics_process(delta):
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ if navigation_agent.is_target_reached():
|
|
|
+ return
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ var current_agent_position : Vector2 = global_transform.origin
|
|
|
+ var next_path_position : Vector2 = navigation_agent.get_next_location()
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ var new_velocity : Vector2 = next_path_position - current_agent_position
|
|
|
+ new_velocity = new_velocity.normalized()
|
|
|
+ new_velocity = new_velocity * movement_speed
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ set_velocity(new_velocity)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ move_and_slide()
|