7 değiştirilmiş dosya ile 4 ekleme ve 15 silme
+ 0
- 4
Makefile
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 0
- 1
conf.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
BIN
tutorials/math/img/vector_cross1.png

+ 0
- 0
tutorials/math/img/tutovec16.png → tutorials/math/img/vector_cross2.png

BIN
tutorials/math/img/vector_dot1.png
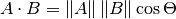
BIN
tutorials/math/img/vector_dot2.png

+ 4
- 10
tutorials/math/vector_math.rst
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||